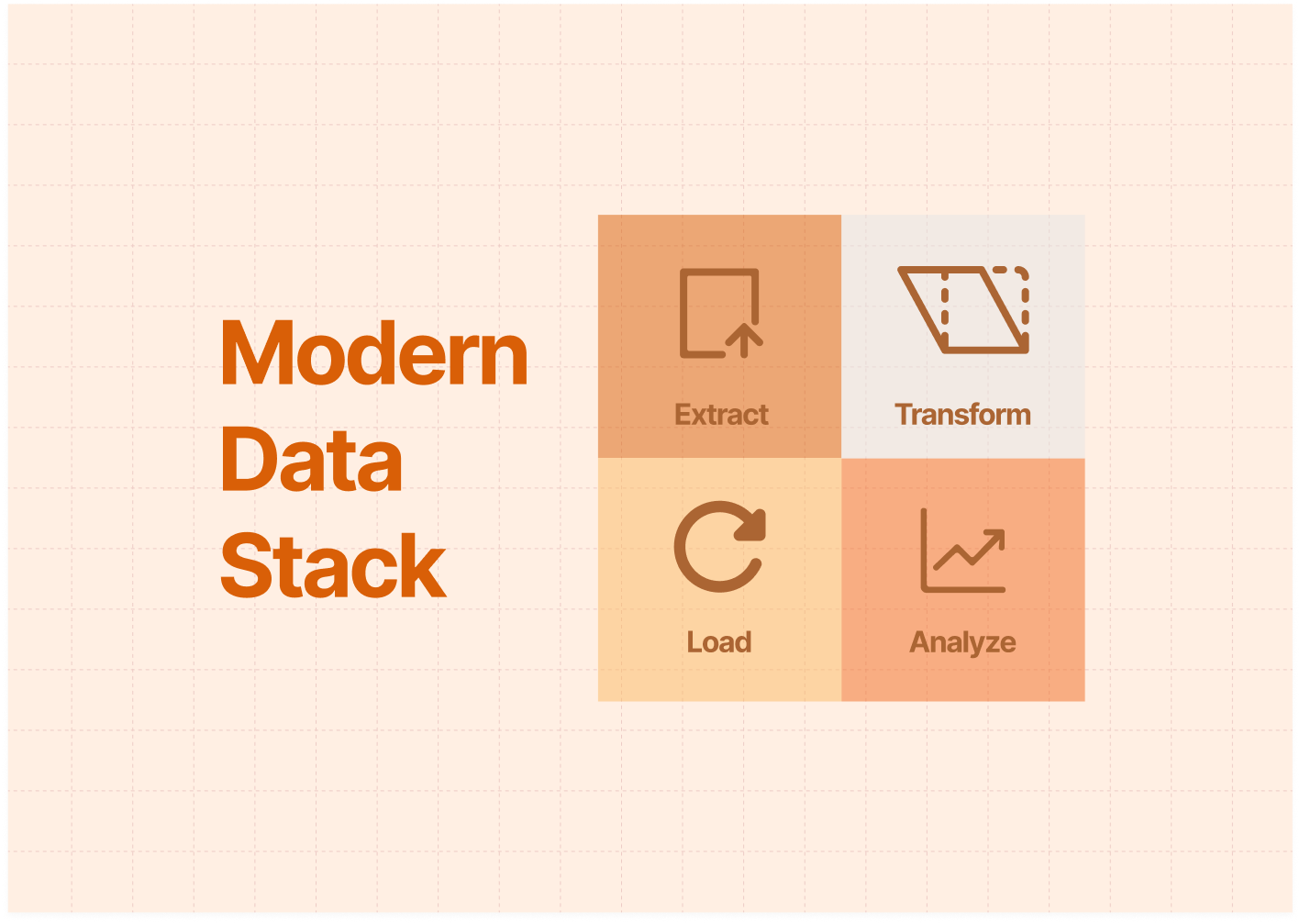
Modern data stack is a technology stack used to collect, process, store, and analyze data, usually composed of multiple tools and platforms. Its purpose is to help businesses process data more effectively and improve the speed and quality of data analysis.
The popularity of modern data stack is related to the modern enterprise's need to process large amounts of data from multiple sources, including websites, mobile applications, social media, sensors, servers, and other databases. Furthermore, businesses need to transform this data into useful insights to make better business decisions.
Traditional data stacks typically require the use of multiple different tools and technologies to complete various stages of data processing. These tools are often incompatible with each other and require a lot of manual configuration and maintenance. On the other hand, modern data stacks are more automated and scalable, usually composed of tools and platforms that can be integrated and upgraded more easily, and generate useful data analysis insights more quickly.
Therefore, modern data stack has become increasingly popular in recent years, especially in large and data-driven enterprises that need to process large amounts of data to improve their business efficiency and competitiveness.
What is Modern Data Stack?
Modern Data Stack refers to a set of modern technologies, tools, and processes that work together to help businesses collect, store, process, and analyze data in real-time, enabling data-driven decision-making.
The modern data stack includes several components, such as:
- Data sources: These are the systems or platforms where data is generated or collected, such as databases, applications, APIs, and IoT devices.
- Data pipelines: These are the tools and processes used to extract data from the data sources, transform it into a usable format, and load it into a data warehouse or data lake. Examples of data pipeline tools include Apache Kafka, Apache NiFi, and Fivetran.
- Data warehouse or data lake: These are the storage systems where data is stored and made accessible for analysis. Examples of data warehouse systems include Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, and Snowflake. Examples of data lake systems include Apache Hadoop and Amazon S3.
- Business intelligence and analytics tools: These are the tools used to explore and analyze data, create dashboards and reports, and gain insights from data. Examples of BI and analytics tools include Tableau, Looker, and Power BI.
- Data governance and security tools: These are the tools used to ensure that data is properly secured, comply with regulations, and manage access to data.
Why is Modern Data Stack so popular?
With the explosive growth of data, enterprises need more data analysis and data science support to help make better decisions. Traditional data analysis processes often require a lot of time and manpower, especially in data extraction and transformation, which often requires technical assistance. The emergence of the Modern Data Stack allows non-technical personnel to easily perform data analysis, thereby improving the efficiency of data analysis and saving costs.
In addition, Modern Data Stack has the following advantages:
- Scalability: Modern data stack technologies are designed to scale seamlessly as data volume and complexity grow, enabling businesses to process and analyze vast amounts of data quickly and easily.
- Real-time data processing: The modern data stack enables businesses to process and analyze data in real-time, providing up-to-the-minute insights and enabling faster decision-making.
- Integration: The modern data stack is designed to be highly integrated, enabling businesses to easily connect data sources, data pipelines, and analytics tools.
- Democratization of data: The modern data stack makes it easier for businesses to share data and insights across teams and departments, enabling a more data-driven culture and empowering individuals to make data-driven decisions.
- Flexibility: The modern data stack is designed to be flexible, enabling businesses to easily add or remove components as their needs change and new technologies emerge.
Why should enterprises pay attention to Modern Data Stack?
- Competitive advantage: The modern data stack enables businesses to extract valuable insights from their data, providing a competitive advantage in a rapidly changing business landscape.
- Improved decision-making: By leveraging the modern data stack, enterprises can make data-driven decisions quickly and effectively, leading to better business outcomes.
- Increased efficiency: The modern data stack automates many of the data processing and analysis tasks, enabling businesses to be more efficient and productive.
- Better customer experiences: The modern data stack enables businesses to better understand their customers, leading to more personalized and targeted experiences that drive loyalty and retention.
- Compliance and governance: The modern data stack includes tools for compliance and governance, ensuring that enterprises remain compliant with regulations and protect the privacy of their customers.
- Innovation: The modern data stack enables enterprises to experiment with new data sources, analysis techniques, and technologies, leading to new insights and opportunities for innovation.
Using Canner as a Data Access Layer of the Modern Data Stack
Enterprises can benefit from data access layers in many ways, including:
- Improved data quality and consistency: The data access layer can help ensure data consistency and accuracy in different tools and applications, reducing the risk of errors and inconsistencies in data analysis.
- Increased production efficiency: The data access layer provides a unified interface for accessing and analyzing data, reducing the need for redundant data processing and improving the efficiency of data analysis. This can increase productivity and reduce costs.
- Enhanced security: The data access layer can help ensure secure and controlled use of data, minimizing the risk of data leakage and unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- Scalability: The data access layer is designed to be highly scalable, able to handle large amounts of data and support multiple concurrent users. This can help enterprises expand their data capabilities over time as needed.
- Flexibility: The data access layer can be customized according to the specific needs and requirements of the enterprise, allowing the organization to use its data in ways that suit its unique needs and goals.
- Better decision-making: By providing a unified interface for accessing and analyzing data, the data access layer can help enterprises generate insights more quickly and make more informed, data-driven decisions.
No reproduction without permission, please indicate the source if authorized.
 Canner
Canner